How to Replace Your Car Starter Battery with LiFePO4: Key Considerations
First, we should determine whether a LiFePO4 battery can be used to start a gasoline-powered car, and the answer is yes. For many vehicles, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are an upgrade over traditional car batteries. For example, LiFePO4 starter batteries provide stronger cranking power, faster charging, built-in emergency start functionality, Bluetooth monitoring, and a longer lifespan compared to conventional batteries. However, not all lithium batteries are suitable for starting gasoline-powered vehicles, so it is crucial to choose a battery specifically designed for this purpose.
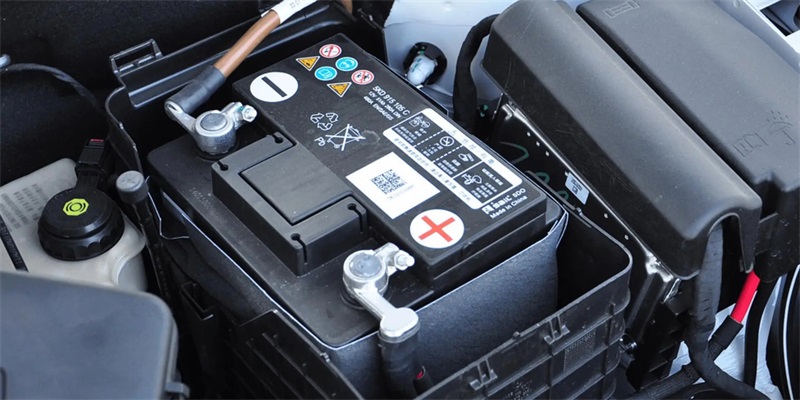

Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a LiFePO4 Car Battery
1. Turn off the vehicle – Ensure your vehicle is completely off and the key is removed from the ignition.
2. Disconnect the old battery – Remove the negative (black) terminal first, followed by the positive (red) terminal. This helps prevent sparks or short circuits.
3. Remove the old battery – Carefully lift it out of the tray. Lead-acid batteries are heavy, so handle with caution.
4. Inspect the battery tray and terminals – Clean any corrosion from the tray and terminal connectors. Since LiFePO4 batteries are lighter and often smaller, you may need additional padding or support to secure them properly.
5. Install the new battery – Place the LiFePO4 battery into the tray and ensure a snug fit. Use spacers or brackets if necessary.
6. Reconnect the terminals – Attach the positive (red) cable first, then the negative (black). Ensure tight and secure connections.
7. Verify secure installation – Make sure the battery does not shift. Prolonged vibration can damage internal components.
8. Power-on test – Start the vehicle to confirm everything operates smoothly. If your battery supports Bluetooth monitoring, use the app to check voltage and state of charge.
Consideration Factors
1. Battery Type Compatibility – If your vehicle currently uses a sealed AGM or other maintenance-free lead-acid battery, a LiFePO4 replacement is more likely to be a direct-fit solution.
2. Alternator Voltage Range – The optimal charging voltage for lithium car starter batteries typically falls between 13.9V and 14.6V, which is common for many LiFePO4 batteries. If your alternator's charging voltage consistently falls below this range, the battery may not fully charge. Charging requirements can vary by battery model, so always check the specifications of the specific battery you plan to use.
3. Charging System Type – Some vehicles use smart alternators that do not always provide sufficient voltage to fully charge certain battery types, such as lithium or AGM deep-cycle batteries. These systems are designed to improve fuel efficiency but may result in undercharging if your battery requires higher or more consistent voltage. If you're unsure what type of system your vehicle has, consult your mechanic or contact us—we can help you find the answer.
4. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) – Ensure your new lithium battery provides at least the same starting power as your existing battery. The Ionic 12V S9 delivers 1,400 amps of cranking current, ensuring reliable starts.
5. Older Vehicle Compatibility – Some classic cars have charging systems specifically calibrated for lead-acid batteries. If you're unsure about compatibility, reach out to us-Energyx, we'll be happy to assist.