How to Charge Lithium Batteries: A Guide to Maximize Lifespan and Safety

In the age of electronics, lithium batteries power over 70% of devices. Unlike lead-acid batteries, they require no regular maintenance like electrolyte refills or terminal cleaning. However, proper charging remains essential to maximize lifespan and safety. This guide provides a clear overview of best practices for charging lithium batteries.
Lithium Battery Basics
Two main types dominate the market: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). Key parameters include:
1. Fully charged voltage per cell: Li-ion: 4.2V and LiFePO4: 3.6V
2. A battery is considered full when the current drops to C/10 and voltage is within 100mV of its maximum.
Charging Process
During charging, lithium ions move back to the cathode while electrons return to the anode, restoring capacity.
Temperature Range-Li-ion: 0°C to 50°C/LiFePO4: 0°C to 60°C
For optimal performance and safety, charge between 10°C and 35°C. Low temperatures slow charging; very cold conditions may prevent it.
Role of the BMS
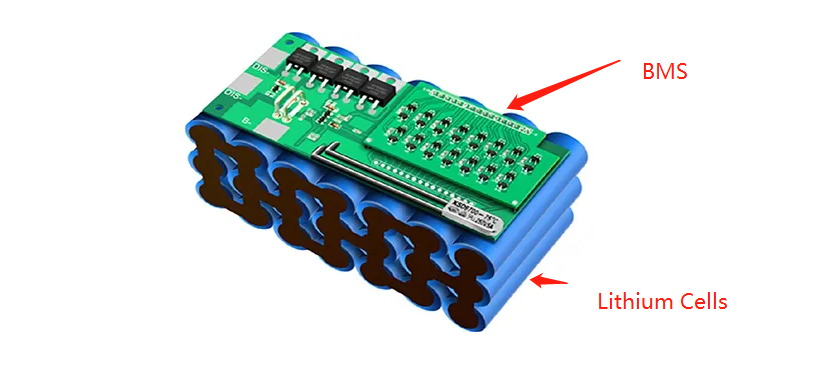
1. A Battery Management System (BMS) is critical. It:
2. Prevents overcharging and over-discharging
3. Monitors temperature and disconnects during extremes
4. Balances cells to extend overall pack life
5. Estimates State of Charge (SoC) and State of Health (SoH)
Why Correct Charging Matters
Although lithium batteries don’t suffer from memory effect and are more flexible than lead-acid, proper charging significantly prolongs service life and ensures safety.
How to Charge Correctly
1. Choose the Right Charger
Select a charger matching your battery chemistry (Li-ion or LiFePO4) and voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V).
Always use a charger designed for your specific battery type.
2. Set the Appropriate Current
Check the battery’s maximum charging current (e.g., 0.5C, 1C). Exceeding this can cause damage.
Example: A 100Ah battery with a 0.5C limit should be charged at ≤50A.
3. Charge Within Suitable Conditions
Temperature: Ideally between 10°C–35°C.
Humidity: Keep below 75% to avoid short circuits.
Step-by-Step Charging
1. Ensure terminals are clean and dry.
2. Connect red (+) cable to positive, then black (-) to negative.
3. Plug in and turn on the charger.
4. Smart chargers stop automatically; manual timers are not needed due to BMS protection.
5. When done, unplug, then disconnect black followed by red.
Charging Time Estimation
For standard chargers:
Charging time (hours) = Battery capacity (Ah) / Charger current (A)
Example: A 100Ah battery charged with a 20A charger takes ≈5 hours.
Storage Charging
If storing lithium batteries, recharge every 3 months to 50–80% capacity to avoid irreversible capacity loss.
Cycle Life
Li-ion: Over 1000 cycles while retaining 80% capacity.
LiFePO4: Over 4000 cycles with 80% capacity retention.
Lithium batteries do not require periodic full discharges. Avoid deep discharges for longest life.

